EOS-984
A highly potent ENT1 antagonist
Intracellular adenosine and its immunosuppressive effects on T cells
High Intracellular Adenosine Drives T cell Suppression in Tumors
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease (SCID) provides genetic validation that the excessive buildup of intracellular adenosine via equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1) induces apoptosis and impairs T cell function.1
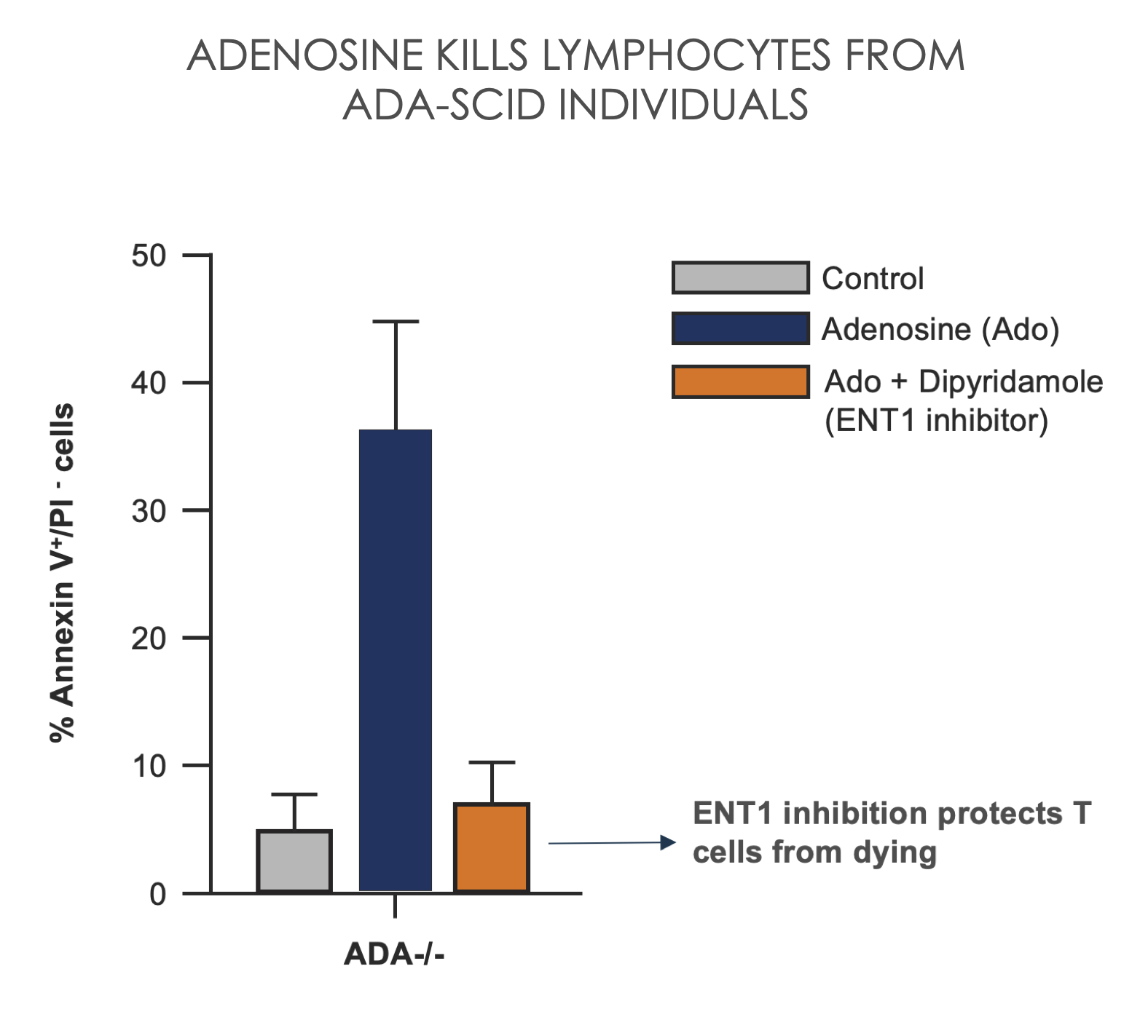
Adapted from Cassani B, et al. Blood. 2008; 111(8):4209-4219.
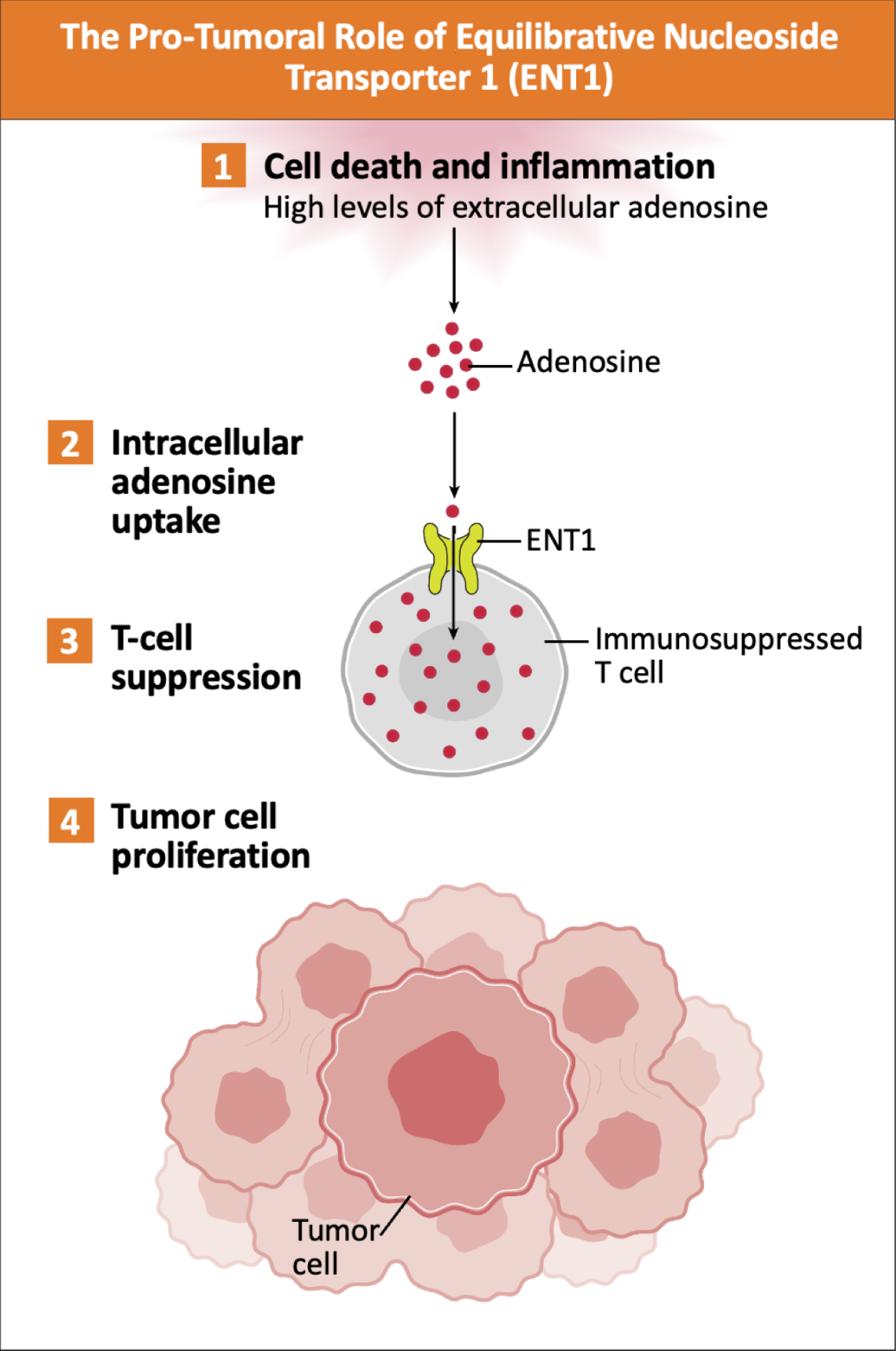
High levels of adenosine are present in most human tumors and its intracellular transport is regulated by equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1).2-4 High intracellular adenosine uptake has been shown to have various immunosuppressive roles in the tumor microenvironment (TME), in particular on T cell metabolism, expansion, effector function, and survival.1,2,3,5-9
Ado, adenosine; ADA, Adenosine Deaminase; ENT1, equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1; SCID, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease; TME, tumor microenvironment.
EOS-984 and its mechanism of action
EOS-984 blocks the intracellular uptake of adenosine into T cells, through the inhibition of ENT1.3 This may relieve adenosine-mediated immunosuppression of tumor-infiltrating T cells, restoring their expansion and effector function.3
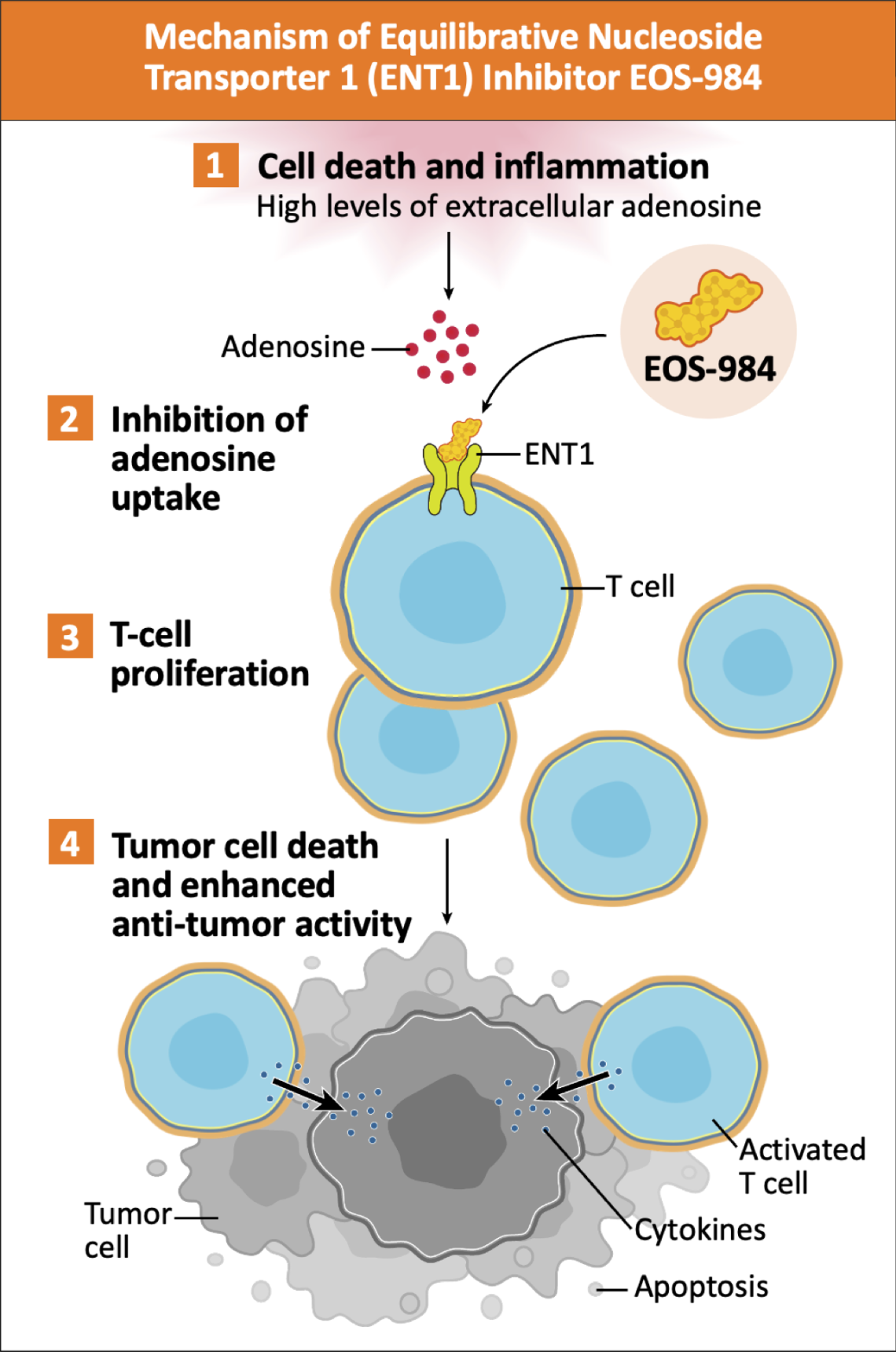
Adapted from Sanders TJ, et al. Poster presented at: AACR Annual Meeting; April 5-10, 2024; San Diego, California and Allard D, et al. Cancer Res. 2025;85(4):692-703.
Blocking intracellular transport of adenosine through ENT1 may be a better approach than other clinical targets of extracellular adenosine (e.g. CD73, A2AR).
EOS-984 provides the most complete rescue of T cell proliferation and pro-inflammatory cytokines in a high-adenosine environment10
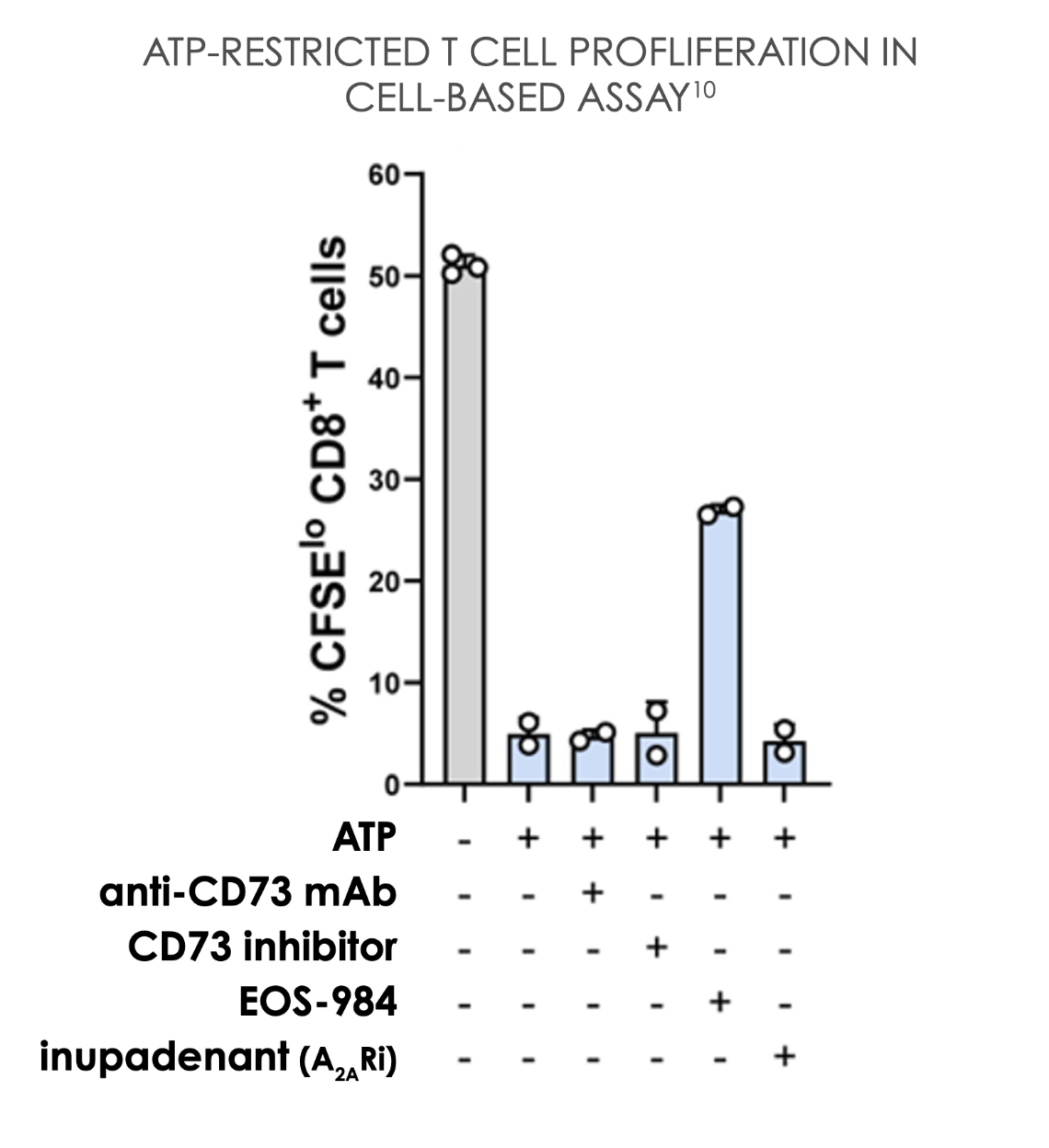
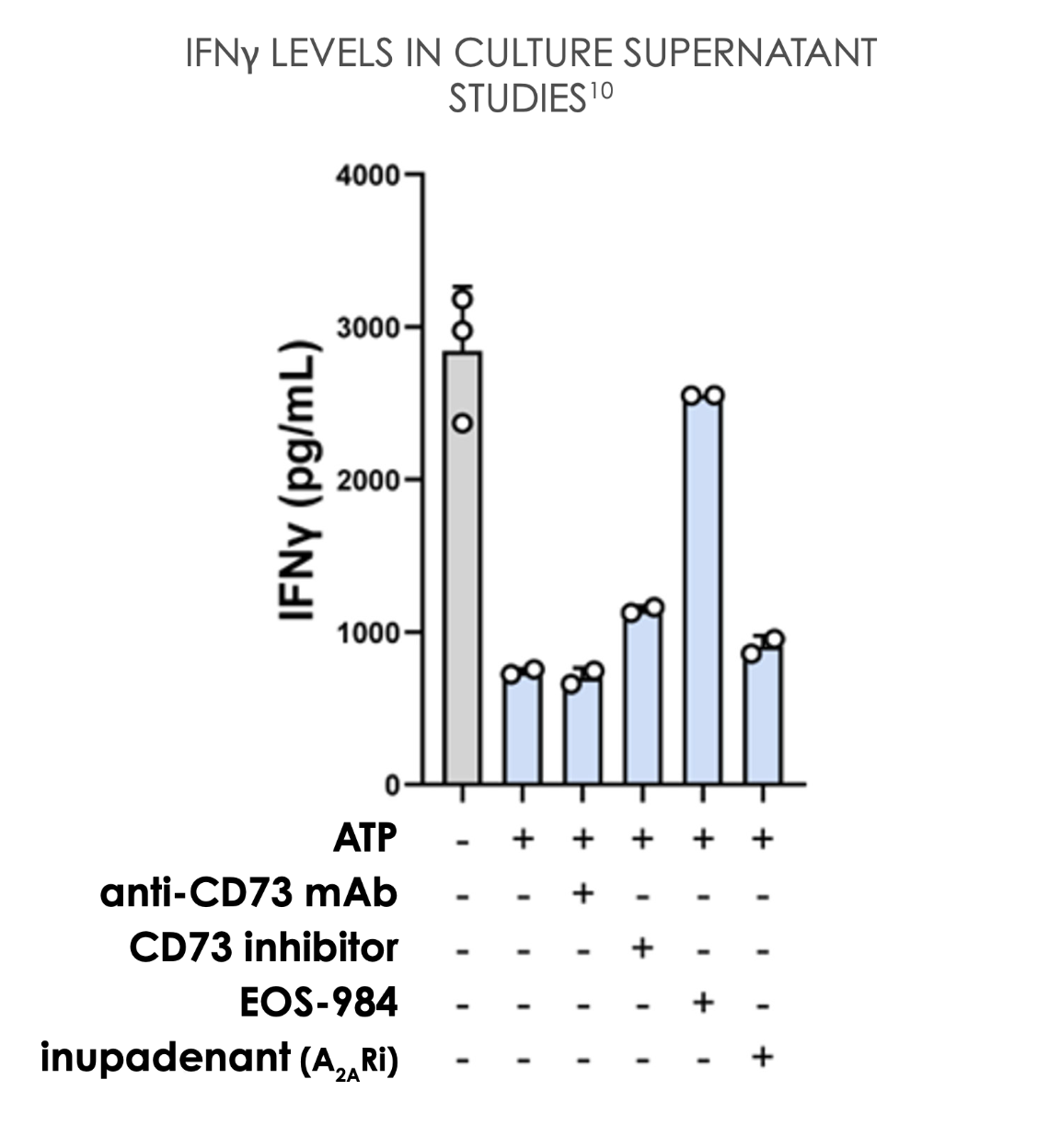
EOS-984 protects tumor-infiltrating T cells from adenosine suppression.2
T cell response restored by blocking ENT1 and further improved when combined with aPD-110
EOS-984 could be explored as a combination partner with other T cell directed therapies beyond aPD-1, including CAR-T cells and bispecific T cell engagers10
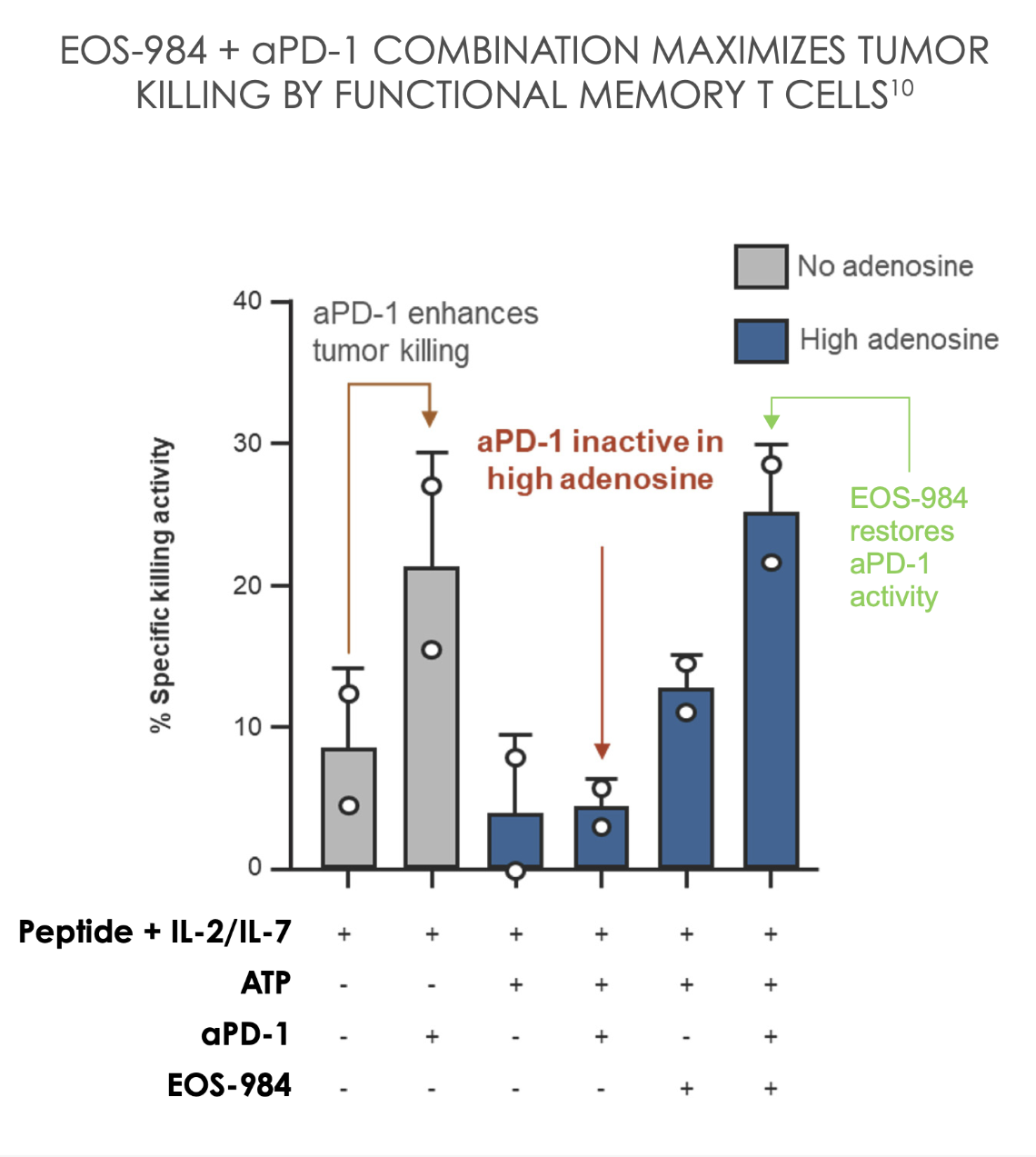
A2AR, adenosine 2A receptor; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; aPD-1, anti-PD-1; CFSE, Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; CAR-T, Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell; CD, cluster of differentiation; ENT1, equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1; IFNγ, interferon γ; IL, interleukin; mAb, monoclonal antibody; pg/mL, picograms per milliliter; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1.
Ongoing clinical trials of EOS-984
iTeos is currently investigating EOS-984 in advanced solid tumors. For more information on this study, please click on the links below:
APT-008: Phase 1 dose escalation and expansion cohort study of EOS-984 as monotherapy and in combination with other anticancer treatments in participants with advanced solid tumors
EOS-984 is a highly potent ENT1 antagonist, designed specifically to target the immunosuppressive effects of intracellular adenosine. Restoration of expansion and effector function of tumor-infiltrating T cells in high adenosine conditions has been demonstrated.10 EOS-984 is currently in Phase 1 clinical development in advanced solid tumors.
- Cassani B, et al. Blood. 2008; 111(8):4209-4219.
- Allard D, et al. Cancer Res. (2025);85(4):692–703.
- Sanders TJ, et al. Poster presented at: AACR Annual Meeting; April 5-10, 2024; San Diego, California.
- Blay J, et al. Cancer Res. 1997;57(13):2602-2605.
- Antonioli et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(12):842-857.
- Allard B, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(10):611-629.
- Xing Z, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6636.
- Cyster JG, Allen CDC. Cell. 2019;177(3):524-540.
- McGettigan SE, Debes GF. Immunol Rev. 2021;303(1):103-118.
- iTeos Therapeutics Inc. (2024). Data on File.
